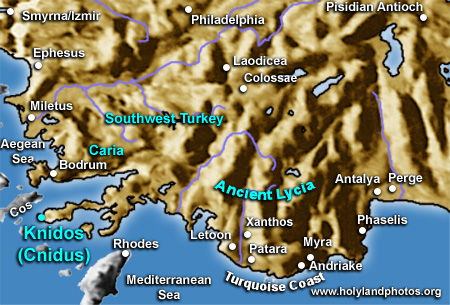
Knidos (Cnidus) was a very important city during the Hellenistic and Roman/Byzantine Periods (ca. 330 B.C. to the seventh century A.D.) located on the western tip of the Daça Peninsula in southwestern Caria (= ancient name; southwestern Turkey). It had trading connections with the eastern Mediterranean, including Egypt, and with Greece and Italy. The main part of the city was built on the southern slope of the peninsula and was connected to the "island" of "Cape Krio" by a series of docks that separated the western harbor (military) from the eastern harbor (commercial).
Because of its location on the very southwest tip of Turkey from here ships could head north into the Aegean, northwest to Greece, or west towards Rome. The apostle Paul passed Cnidus on his voyage to Rome (Acts 27:7).
Among its many temples was the Temple of Aphrodite (Venus) with its famous statue of Aphrodite (now lost) by the sculptor Praxiteles.
The site has been extensively excavated and significant statuary was carted off to the British Museum in the 19th century.